VIRTUAL RELEASE OF THE ANNUAL AGRICULTURAL SURVEY RESULTS, 2022
MEDIA ADVISORY 24 November 2023 VIRTUAL RELEASE OF THE ANNUAL AGRICULTURAL SURVEY RESULTS, 2022 The Statistician-General, Mr Risenga Maluleke will release the annual Agricultural Survey results, 2022 at a virtual press briefing on Wednesday, 29 November 2023. The Agricultural Survey covers the activities of commercial farms in South Africa which are registered for read more »

Participation in the Annual Agricultural Survey 2014
The Annual Agricultural Survey collects and provides statistics on the farming sector across the country. Statistics collected form the basis for planning, monitoring, evaluation, research and decision-making in both private and public institutions for the agricultural sector as a whole. Statistics South Africa (Stats SA) appeals to selected farmers to participate in the Annual Agricultural read more »
Media Release: Community Survey 2016, Agricultural Households
MEDIA RELEASE 27 January 2017 Community Survey 2016, Agricultural Households The number of South African households engaged in agricultural activities decreased between 2011 and 2016. There were 550 000 (19,1%) fewer agricultural households in 2016 (2,33 million) than in 2011 (2,88 million).This decline was mainly due to the drought experienced throughout the country read more »
Media invite: Statistician-General to release the Community Survey 2016, Agricultural Households report
Media advisory 25 January 2016 The Statistician-General of South Africa, Dr Pali Lehohla, will release the read more »

Employment dips in SA’s formal non-agricultural sector during Q4:2023
Statistics South Africa has committed to provide up-to-date and reliable statistics derived from the Quarterly Employment Statistics (QES) survey to ensure accurate information for users and policymakers. The results of the QES, Q4:2023 are derived from the 2023 sample, which was drawn in April 2023. This annual process typically impacts employment and gross earnings levels. read more »

Formal non-agricultural sector jobs rise in the third quarter of 2023
According to the Quarterly Employment Statistics (QES, Q3:2023) survey released by Statistics South Africa (Stats SA), total employment in the formal non-agricultural sector increased by 31 000 in the third quarter of 2023, bringing the level of employment to almost 10,2 million. The survey showed that 256 000 jobs were added between September 2022 and September read more »

Jobs in the non-agricultural sector rise in the second quarter of 2023
The formal non-agricultural sector added 39 000 jobs in the second quarter of 2023, reaching almost 10,1 million jobs. According to the latest Quarterly Employment Statistics (QES, Q2:2023) survey released by Stats SA, there was a year-on year net increase of 104 000 jobs. Between March and June 2023, total (full- and part-time) employment rose read more »

Employment drops in Formal Non-Agricultural Sector in Q1 of 2023
According to the Quarterly Employment Statistics (QES, Q1:2023) survey released by Statistics South Africa (Stats SA), total employment in the formal non-agricultural sector decreased by 21 000 in the first quarter of 2023, bringing the level of employment to almost 10 million. The survey showed that 97 000 jobs were lost between March 2022 and March read more »

SA formal non-agricultural sector jobs rise in fourth quarter of 2022
According to the Quarterly Employment Statistics (QES, Q4:2022) survey released by Statistics South Africa (Stats SA), total employment in the formal non-agricultural sector increased by 48 000 in the fourth quarter of 2022, bringing the level of employment to almost 10 million. The survey showed that 94 000 jobs were lost between December 2021 and December read more »
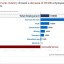
Third quarter jobs rise in SA formal non-agricultural sector
According to the Quarterly Employment Statistics (QES, Q3:2022) survey released by Statistics South Africa (Stats SA), total employment in the formal non-agricultural sector increased by 10 000 in the third quarter of 2022, bringing the level of total employment to approximately 10 million. The survey showed that jobs increased by 31 000 between September 2021 and read more »



